Antibiotic Breakthrough – Researchers Create New Molecule To Tackle Antimicrobial Resistance
- Uncategorized
- No Comment
- 170
Researchers at Maynooth University have developed a new molecule designed to combat drug-resistant bacteria.
An international team, including researchers from Maynooth University, has developed a novel molecule with the potential to combat drug-resistant bacteria.
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is a phenomenon where bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites evolve over time, becoming immune to medications. This resistance makes infections more difficult to cure, elevating the risk of prolonged illness and mortality. Given the prediction that conventional antibiotics will largely lose their effectiveness by 2050 due to escalating AMR levels, finding new methods to eradicate bacteria has become a critical scientific priority.
Supramolecular Chemistry: A Key to Combating AMR
The research harnessed the principles of supramolecular chemistry, a niche scientific area that explores interactions between molecules, to achieve the breakthrough. Most importantly, the study uncovered molecules that are efficient at killing bacteria but whose toxicity to healthy human cells is very low.
The new research is described in the prestigious journal Chem, to coincide with World AMR Awareness Week which runs from 18-24 November. This global campaign, run by the World Health Organization, aims to raise awareness and understanding of AMR in the hope of reducing the emergence and spread of drug-resistant infections.
More than 1.2 million people, and potentially millions more, died in 2019 as a direct result of antibiotic-resistant bacterial infections, according to the most comprehensive estimate to date of the global impact of AMR. This research may pave the way for new approaches to tackle this problem that kills more people annually than HIV/AIDS or malaria.
Lead researcher Luke Brennan of Maynooth University’s Department of Chemistry said: “We are discovering new molecules and looking at how they bind to anions, which are negatively charged chemicals that are extremely important in the context of the biochemistry of life. We are laying the fundamental foundations that could prove useful in combatting various diseases from cancer to cystic fibrosis.”
‘Trojan Horse’ Approach to Combat Resistant Bacteria
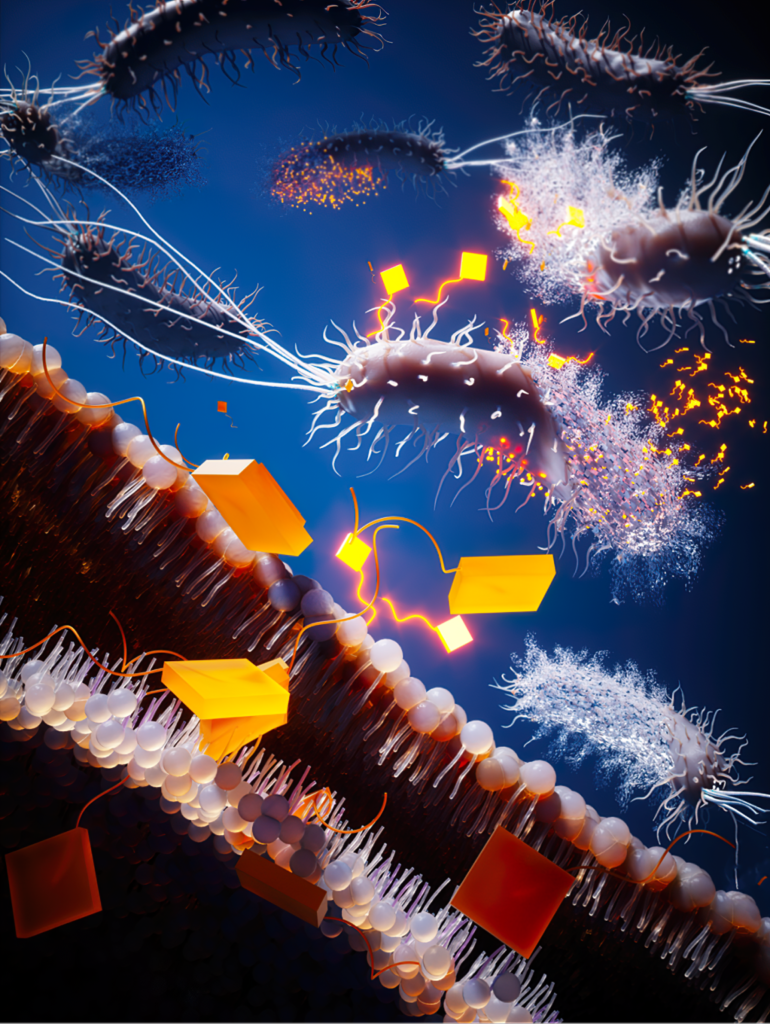
The work is based on the use of synthetic ion transporters and is the first time that researchers have demonstrated that an influx of salt (sodium and chloride ions) into the bacteria can cause a series of biochemical events that lead to bacterial cell death – even in strains that are resistant to currently available antibiotics such as methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA).
Study co-author Dr Robert Elmes of Maynooth University’s Kathleen Lonsdale Institute for Human Health Research, says: “This work shows how using our approach, a sort of ‘trojan horse’ that causes an influx of salt into cells, we can effectively kill resistant bacteria in a way that counteracts known methods of bacterial resistance.”
Bacteria work hard to maintain a stable concentration of ions inside their cell membranes, and when this delicate balance is disrupted it wreaks havoc on normal cell function and the cells cannot survive.
Elmes continued: “These synthetic molecules bind to chloride ions and wrap it up in a ‘fatty blanket’ that allows it to easily dissolve in the bacteria’s membranes, bringing the ions along for the ride and disrupting the normal ionic balance. The work is a great example of foundation knowledge in chemistry fundamentals impacting on unmet needs in human health research.”
Prof Kevin Kavanagh, a microbiologist in Maynooth University’s Department of Biology commented: “The rising incidence of infections by drug-resistant bacteria is a major concern. This work is an example of chemists and biologists working together to pioneer the development of new antimicrobial agents with significant future potential.”
Such results pave the way for the potential development of anion transporters as a viable alternative to currently available antibiotics, something urgently required as the problem of AMR continues to rise.
By MAYNOOTH UNIVERSITY